运行以下程序,输出的结果是?( )
class A(): def __init__(self,x): self.x=x+1 def b(self): return self.x*self.x t=A(3) print(t.b())
9
12
7
16
运行以下程序,输出的结果是?( )
运行以下程序,输出的结果是?( )
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('t1.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
conn.execute("DELETE from user")
cursor.execute('insert into user (id, name) values (\'1\', \'张三\')')
cursor.execute('insert into user (id, name) values (\'2\', \'李四\')')
cursor.execute('insert into user (id, name) values (\'3\', \'王二\')')
cursor.execute('insert into user (id, name) values (\'4\', \'刘五\')')
conn.commit()
cursor.execute('select id,name from user')
values = cursor.fetchone()
values = cursor.fetchone()
print(values)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
('4', '刘五')
('1', '张三')
('2', '李四')
('3', '王二')
以下SQLite语句可以修改记录的是?( )
cursor.execute('insert into user (id, name) values (\'1\', \'张三\')') |
cursor.execute('update user set name = "吴吴" WHERE ID = 4') |
cursor.execute('select id,name from user')
conn.execute("DELETE from user") |
SQLite函数中,以下语句的作用是?( )
values = cursor.fetchmany(2)
print(values)
输出前两条记录
输出第2条记录
输出后两条记录
输出中间两条记录
关于SQLite,说法错误的是?( )
commit()功能是提交当前的所有事务。如果没有提交,程序自上次提交后的所有操作是不可见的
execute()功能是执行SQL语句
fetchall()功能是获取查询结果中所有的记录,返回类型为列表
close()功能是关闭数据库连接,将自动调用commit()以保存所有更改
有一个叫做Animal的类,请问下面哪个选项是正确的创建子类Cat的语法?( )
class Cat(Animal):
class Cat extends Animal:
class Cat inherits Animal:
class Cat is Animal:
下面的代码定义了一个Circle类,用于表示圆形的信息。请问执行下面的代码后,会输出什么?( )
class Circle(): def __init__(self, radius): self.pi=3.14 self.radius = radius #半径 def area(self): #面积 return self.pi * self.radius ** 2 def perimeter(self): #周长 return 2 * self.pi * self.radius c = Circle(4) print(c.area()) print(c.perimeter())
25.12
50.24
没有输出
50.24
25.12
会报错
下面哪个代码可以创建一个名为cat的实例,属于Animal类,有color和sound两个属性,分别赋值为"black"和"meow"?( )
cat = Animal()
cat = Animal()
cat.color = "black"
cat.sound = "meow"
cat.color = "black"
cat.sound = "meow"
cat = Animal()
cat = new Animal()
cat.color = "black"
cat.sound = "meow"
以只读的方式打开文本文件‘a.txt’的代码是?( )
f=open('a.txt','r')
f=open('a.txt','w')
f=open('a.txt','a')
f=open('a.txt','r+')
有如下Python代码:
f=open('RGB.txt','r')
a=f.readlines()
代码中变量a的数据类型是?( )
字符串
数组
元组
列表
文本文件'a.txt'为空文件,执行以下Python后,'a.txt'文件中的内容是?( )
n=1
f=open('a.txt','a')
while n<=6:
f.write(str(n))
n+=1
f.close()
123456
6
空
1
文件a.txt中的内容如图所示:
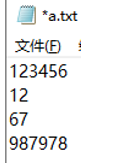
执行如下Python代码,输出的结果是?( )
s=0
with open('a.txt') as f:
a=f.readlines()
for i in a:
if len(i)>3:
s+=1
print(s)
1
2
3
4
下面代码的输出结果是?( )
import numpy as np x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) print(x[2:4])
[3 4]
[2 3]
[2 3 4]
[2 4]
下面代码的输出结果是?( )
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) print(arr.sum())
3
4
6
10
下面代码的输出结果是?( )
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.plot(x, y1)
plt.xlabel('x轴')
plt.ylabel('y1轴')
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.scatter(x, y2, color='r')
plt.xlabel('x轴')
plt.ylabel('y2轴')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
显示一个子图,包含一个包含折线图的区域和一个包含散点图的区域
显示一个子图,包含一个包含折线图和散点图的混合图形
显示两个子图,分别包含折线图和散点图
不显示任何内容
下面代码的输出,最合理的选项结果是?( )
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('x轴')
plt.ylabel('y轴')
plt.title('简单折线图')
plt.show()
显示一个简单的折线图
显示一个已经标注了标题、x轴和y轴标签的简单折线图
显示一个已经标注了 x 轴和 y 轴标签的简单折线图
不显示任何内容
以下Python代码为在tk上绘制一个图形,请问绘制的图形是?( )
import tkinter as tk root = tk.Tk() canvas = tk.Canvas(root, width=300, height=300) canvas.create_rectangle(100, 100, 200, 200, outline="red") canvas.pack() root.mainloop(
100*200的矩形
300*300的矩形
100*100的矩形
200*100的矩形
有如下Python代码,如图状态下,点击提交按钮,文本框内显示的内容为?( )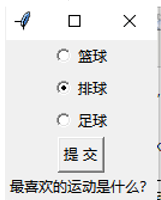
import tkinter as tk
def show_selected_option():
selection = variable.get()
p={1:"篮球",2:"排球", 3:"足球"}
label.config(text=f"最喜欢的运动是 {p[selection]}")
root = tk.Tk()
options = [("篮球", 1), ("排球", 2), ("足球", 3)]
variable = tk.IntVar()
for text, value in options:
tk.Radiobutton(root, text=text, variable=variable, value=value).pack()
button = tk.Button(root, text="提 交", command=show_selected_option)
label = tk.Label(root, text="最喜欢的运动是什么?")
button.pack()
label.pack()
root.mainloop(
最喜欢的运动是排球
最喜欢的运动是篮球
最喜欢的运动是足球
最喜欢的运动是2
在tkinter中添加一个按钮的代码是?( )
button = tk.Label(root, text="Hello")
button = tk.Entry(root)
button = tk.Button(root, text="Click")
button = tk.Checkbutton(root, text="Check me")
在tkinter中设置控件widget的背景颜色改为红色的方法是?( )
`widget.bg_color = "red"`
`widget.background = "red"`
`widget.set_bg_color("red")`
`widget.config(bg="red")`
下列程序的运行结果是 [20 16 12 8 4],请填空?( )
import numpy as np x1 = np.arange( , , ) print(x1)
20,0,4
20,0,-4
0,20,4
0,20,-4
下列程序的运行结果为:2,请填空?( )
import numpy as np a = np.arange(0,12).reshape(3,4) print(
a.shape()
a.shape
a.ndim()
a.ndim
在一个Python表示的二维数组a=[[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]的第二列位置插入一列新的数据后,能够实现访问该数组中数据8的语句是?( )
a[1][3]
a[2][3]
a[1][4]
a[2][4]
以下程序实现:把'xiaoming'的个人信息填到family的csv文件中,再读取出来。空格处应填?( )
import json
import csv
fam = {'name':'xiaoming','age':18,'gender':'nan'}
with open('family.csv','w') as f:
json. (fam,f)
with open('family.csv','r') as f1:
read1 = json. (f1)
print(read1
reader,writer
writer,reader
dump,load
load,dump
在Python中使用JSON库进行JSON数据的处理,以下哪个选项描述正确的是?( )
使用json.dumps()函数可以将Python对象转换为JSON字符串
使用json.write()函数可以将Python对象写入JSON文件
使用json.decode()函数可以将JSON字符串解码为Python对象
使用json.parse()函数可以将JSON字符串解析为Python对象
在SQLite操作中,语句conn = sqlite3.connect('test1.db')功能是创建一个新数据库test1.db。如果test1.db已经存在,程序将报错。( )
当创建一个子类时,它会自动获得父类的所有属性和方法。( )
关于类与对象的描述,定义方法__init__() 时,self 必不可少,还必须位于其他形参的后面。( )
有如下代码:
with open('RGB.jpg','rb') as f:
a=f.read()
这段代码可以将图像文件RGB.jpg的二进制数据存储在变量a中。( )
有如下代码
f=open('123.txt','w')
f.write('hello')
f.close()
执行代码后,文件123.txt中的原有内容将会被覆盖。( )
import numpy as np
dt = np.dtype('i8')
print(dt)上面代码的输出结果是int64。( )
下列代码中plt.bar(x, y) 函数用于散点图。( )
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x = np.array(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']) y = np.array([3, 7, 2, 5]) plt.bar(x, y) plt.show()
运行如下代码,点击按钮Greet后label框内显示“Hello, World!”字样。( )
import tkinter as tk def greet(): label.config(text="Hello, World!") root = tk.Tk() label = tk.Label(root, text="") button = tk.Button(root, text="Greet", command=greet) label.pack() button.pack() root.mainloop()
Python中的JSON库提供了将自定义对象直接转换为JSON格式的功能。( )
创建一个二维数据的NumPy数组:
data = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
访问数组中第二行第三列的元素的表示方式是value=data[2, 3]。( )
编写一个类`Circle`,包含两个属性`radius`和`color`,以及四个方法`get_area()`、`get_circumference()`、`get_diameter()`和`print_info()`,分别用于计算圆面积、圆周长、圆直径,并打印出圆的半径和颜色。
代码如下,请补全代码。
class Circle:
def __init__(self, radius, color):
①
self.color = color
def get_area(self): #圆面积
return ②
def get_circumference(self): #圆周长
return ③
def get_diameter(self):
return 2 * self.radius
def print_info(self):
print("Radius:", self.radius)
print("Color:", self.color)
circle = Circle(5, "red")
④ #输出圆的半径和颜色
print("Area:", circle.get_area())
print("Circumference:", circle.get_circumference())
print("Diameter:", circle.get_diameter())
学生表操作题
建立学生表,将学号设置为主键,实现对数据的添加和查找。(无需运行通过,写入代码即可)
import sqlite3
con = sqlite3. ① ('./student.db')
cur = ②
sql ='''
③ IF NOT EXISTS Stu (
id INTEGER ④ AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT,
age INTEGER,
clas TEXT)
'''
cur.execute(sql)
con.commit()
sql = '''
⑤ (name,age,clas) VALUES(?,?,?)
'''
cur.execute(sql,('张三',16,'二三班'))
con.commit()
统计单词问题
统计英文文本中出现的不同单词个数:读取只包含英文和标点的文件'/data/abc.txt',文件中单词和单词之间用1个空格或标点符号隔开,文末以标点符号结尾,在区分单词大小写的情况下,输出该文本中所出现的不同单词个数。
实现上述功能的Python程序如下,请在划线处填入合适的代码。
f=open('/data/ ① ','r')
text=f.read()
lst=[]
s=""
def judge( ② ):
if st in lst:
return False
else:
return True
for i in range(len(text)):
c= ③
if"a"<=c<="z" or"A"<=c<="Z":
s=s+c
else:
if judge(s):
lst.append(s)
s=""
print("出现的不同单词个数为:",len(lst))